A canonical link element is an HTML code element that helps prevent issues involved with duplicate content. This specification will indicate the following URL as the preferred URL for the object and also in search results. Using canonical links will increase the chance for important pages being crawled, indexed and ranked.
How to Use Canonical Links
A canonical link element is placed by specifying “canonical” in the “rel” field of the HTML link tag. The link tag of a canonical link must appear in the <head> section of the HTML page or as an HTTP response header.
Significance of Canonical Links
When search engines go through many links with identical or similar content, it can cause a number of search engine optimization problems related to duplicate content. If search crawlers have to go through too much duplicate content, they may miss the unique content on the individual pages. Large-scale duplication may dilute a site’s rank when appearing on search engines such as Google or Bing. Even if the content shows up when searched, the wrong URL may be chosen as the “original,” directing users to the unpreferred link.
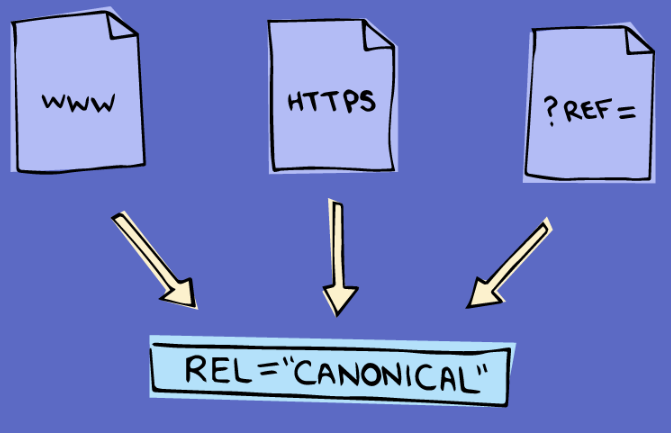
For example, all the following links lead to the same page:
When visiting the site, these links lead to the same content and are essentially the same site. However, to a search engine, these websites are all treated as unique links. Especially on websites with large numbers of parameters for searches, such as online shopping sites, there may be hundreds of these links that, unknowing to the webmaster, lead to the same page.
Important Info for Canonical Links
- Homepages should be canonicalized in addition to subsites in a website.
- Code should be spot-checked for mistakes in canonicalization that can lead to a unique canonicalized link for each version of the URL, defeating the purpose of canonicalization.
- Canonical links can be self-referencing. Similarly, there can be one canonical link for multiple pages, but multiple pages should never have cross-referencing canonical links. For example, A’s canonical link can be B and B’s canonical link can be B, but A’s canonical link should not be B if B’s canonical link is A.
- A page that is very different from another page should not be canonicalized to the other page. A search engine will most likely ignore the canonicalization if it senses that.
While the canonical link element can be helpful for webmasters or website owners, Google’s webspam team has specified that the search engine actually prefers 301 redirects rather than canonical tags. This is because Google’s spiders may choose to ignore canonical links if beneficial.
Works Consulted
“Canonicalization,” SEO Learning Center, Moz, n.d.
“What is a Canonical Link Element?” The Digital Project Manager – Web and E-Commerce, The Digital PM, 20 July 2016.






![Why Is SEO Expensive? A Realistic Review Of SEO Pricing In Singapore [2024]](https://www.firstpagedigital.sg/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/SEO-Pricing.jpg)









